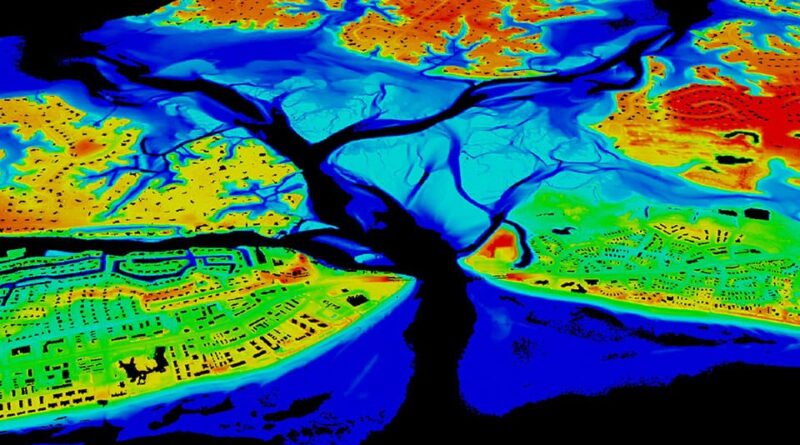
LiDAR survey reports to augment water in forest areas
Context:
Union Environment Minister released LiDAR-based reports mapping out the water requirement within forest areas in 10 states.
Key Highlights
- The LiDAR (Light Detection And Ranging) technology was used to create 3-D images of the project areas to recommend soil and water conservation structures.
- The surveys were carried out in forest areas in Assam, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Goa, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Manipur, Nagaland, and Tripura.
- It is a first of its kind and a unique experiment using LiDAR technology which will help augment water and fodder in jungle areas thereby reducing human-animal conflict.
- The project was awarded to WAPCOS, a PSU under the Jal Shakti Ministry for implementation in 26 states.
About LIDAR
Light detection and ranging (LiDAR) is a remote sensing method that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure ranges to the Earth.
- LiDAR uses a pulsed laser to calculate an object’s variable distances from the earth surface.
- LiDAR follows a simple principle — throw laser light at an object on the earth surface and calculate the time it takes to return to the LiDAR source. Given the speed at which the light travels (approximately 186,000 miles per second), the process of measuring the exact distance through LiDAR appears to be incredibly fast.
- These light pulses — put together with the information collected by the airborne system — generate accurate 3D information about the earth surface and the target object.
- There are three primary components of a LiDAR instrument — the scanner, laser and GPS receiver. Other elements that play a vital role in the data collection and analysis are the photodetector and optics.
- Two Types: Airborne LiDAR installed on a helicopter or drone for collecting data and Terrestrial LiDAR systems installed on moving vehicles or tripods on the earth surface for collecting accurate data points.
Applications of LiDAR
- Agriculture: LiDAR can be used to create 3D elevation maps of a particular land. This can be converted to create slope and sunlight exposure area maps. This information can be used to identify the areas which require more water or fertilizer and help the farmers to save on their cost of labor, time and money.
- River Survey: Water penetrating green light of the LiDAR can be used to see things underwater and helps create a 3D model of the terrain. It helps in monitoring the floodplains.
- Modelling Pollution: LiDAR wavelength is shorter and it operates in ultraviolet, visible region or near infrared. This helps to image the matter which is of the same size or larger than the wavelength. So LiDAR can detect pollutant particles of carbon dioxide, Sulphur dioxide, and methane.
- Archeology and Building Construction: LiDAR plays an important role for the archeologist to understand the surface. LiDAR can detect micro-topography that is hidden by vegetation which helps archeologists to understand the surface.
- Ground-based LiDAR technology can be used to capture the structure of the building. This digital information can be used for 3D mapping on the ground which can be used to create models of the structure.
- Oceanography: Other than locating objects, LiDAR is also used for calculating phytoplankton fluorescence and biomass in the ocean surface, which otherwise is very challenging.
- Astronomy: LiDAR is also capable of mapping the surfaces of celestial bodies – it was used to generate a precise global topographic survey of Mars in 2001.
- Autonomous vehicles: LiDAR sensors determine the exact position of obstacles in the surrounding environment, generating data that will steer vehicles in the right direction to avoid making an impact.
- Green Energy: LiDAR attached to the turbine itself is used to calculate the direction and strength of wind, and if necessary will change the direction of the blade in order to generate more power.
Advantages of using LiDAR
- Data can be collected quickly and with high accuracy: LiDAR is an airborne sensing technology which makes data collection fast and comes with extremely high accuracy as a result of the positional advantage.
- Surface Data has a higher sample density: LiDAR gives a much higher surface density compared to other methods of data collection such as photogrammetry. This improves results for some kinds of applications such as flood plain delineation.
- Capable of collecting elevation data in a dense forest: LiDAR technology is capable of collecting elevation data from a densely populated forest thanks to the high penetrative abilities. This means it can map even the densely forested areas.
- Can be used day and night: LiDAR technology can be used day and night thanks to the active illumination sensor. It is not affected by light variations such as darkness and light. This improves its efficiency.
- It is not affected by extreme weather: LiDAR technology is independent of extreme weather conditions such as extreme sunlight and other weather scenarios. This means that data can still be collected under these conditions and sent for analysis.
- Does not have any geometry distortions
- It can be integrated with other data sources
- It has minimum human dependence
- Surface data has a higher sample density
- Can be used to map inaccessible and featureless areas
Disadvantages of LiDAR
- High operating costs in some applications
- Ineffective during heavy rain or low hanging clouds because of the effects of refraction. However, the data collected can still be used for analysis.
- Degraded at high sun angles and reflections
- Unreliable for turbulent breaking waves as it will affect the reflection of pulses
- No International protocols
- Very large data sets which are difficult to interpret.
- The laser beams may affect human eye in cases where the beam is powerful
- Requires skilled data analysis techniques
- Low operating altitude of between 500-2000m
Source: PIB