National Education Day in India
Contents
National Education Day in India
National Education Day is celebrated annually on November 11 in India to honor the birth anniversary of Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, the first Minister of Education in independent India. This observance, initiated by the Government of India in 2008, serves to recognize Azad’s significant contributions to the country’s educational framework and to promote awareness about the importance of education in national development.
Historical Context
Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, born on November 11, 1888, was a prominent freedom fighter, scholar, and a key figure in shaping India’s education policy post-independence. His tenure as the education minister from 1947 to 1958 was marked by foundational reforms aimed at making education accessible to all. He was instrumental in establishing several prestigious institutions, including the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) and the University Grants Commission (UGC), which have become cornerstones of higher education in India.
Significance of National Education Day
The observance of National Education Day serves multiple purposes:
– Commemoration: It honors Azad’s legacy and his vision for an inclusive education system.
– Awareness: It raises awareness about the critical role of education in empowering individuals and fostering societal progress.
– Reflection: The day provides an opportunity to reflect on current educational challenges and strategize improvements.
In recent years, events such as seminars, workshops, and discussions are organized across educational institutions to engage students and educators in dialogues about educational policies and innovations.
Statistics Related to Education in India
Education is a fundamental right enshrined in the Indian Constitution. Here are some key statistics that highlight the current state of education in India:
– As per the National Statistical Office (NSO) report, the Gross Enrollment Ratio (GER) for higher education in India stands at approximately 27% as of 2021.
– The literacy rate has improved significantly over the years, reaching around 77.7% as per the latest census data.
– The Right to Education Act, enacted in 2009, mandates free and compulsory education for children aged 6 to 14 years, aiming to bridge educational disparities.
Government Initiatives for Education
The Indian government has launched several initiatives aimed at improving educational access and quality:
– Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan: A holistic program aimed at ensuring inclusive and equitable quality education from preschool to senior secondary levels.
– Pradhan Mantri Vidya Lakshmi Karyakram: This initiative provides financial support for students pursuing higher education through loans.
– Digital India Initiative: Aims to enhance digital infrastructure in schools and promote e-learning resources.
Additionally, programs like Beti Bachao Beti Padhao emphasize girls’ education, reflecting a commitment to gender equality in educational opportunities.
PM SHRI: Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi approved the PM SHRI Schools (PM Schools for Rising India) scheme on 7th September 2022. The initiative aims to strengthen over 14,500 schools across India, showcasing the components of the National Education Policy 2020. The scheme will foster quality education, cognitive development, and 21st-century skills in students. With a total project cost of ₹27,360 crore, it will be implemented over five years (2022-2027), with a central share of ₹18,128 crore.
Samagra Shiksha: Aligned with the NEP 2020 recommendations, Samagra Shiksha aims to provide quality education with an inclusive and equitable classroom environment for all children, addressing their diverse backgrounds and needs. The scheme, launched on April 1, 2021, will continue for five years, ending on March 31, 2026. It focuses on fostering active participation and enhancing academic abilities across various student groups.
PRERNA: Launched its pilot phase from January 15, 2024, to February 17, 2024, at a vernacular school in Vadnagar, Gujarat. The initiative is a week-long residential program designed for selected students from class IX to XII. It aims to offer an experiential and inspirational learning experience, blending heritage with innovation through state-of-the-art technology. Each week, a batch of 20 students (10 boys and 10 girls) from across the country will participate in the program.
ULLAS: Also known as Nav Bharat Saaksharta Karyakram (New India Literacy Programme – NILP), ULLAS was launched by the Government of India for the period FY 2022-2027. This centrally sponsored initiative aligns with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and aims to empower adults aged 15 and above, especially those who missed out on formal schooling. The program seeks to enhance their literacy, enabling them to better integrate into society and actively contribute to the nation’s development.
NIPUN Bharat: The National Initiative for Proficiency in Reading with Understanding and Numeracy (NIPUN Bharat) was launched by the Department of School Education & Literacy on 5th July 2021. The mission aims to ensure that every child in the country achieves foundational literacy and numeracy by the end of Grade 3, with a target completion by 2026-27.
Vidya Pravesh: The VIDYA PRAVESH guidelines for the Three-month Play-based School Preparation Module for Grade-I children were released on 29th July 2021. The initiative aims to provide a warm and welcoming environment for children entering Grade-I, ensuring a smooth transition and fostering a positive learning experience.
Vidyanjali: The School Volunteer Management Program, launched by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi on 7th September 2021, aims to enhance the quality of education in schools by fostering community involvement, and encouraging contributions from corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives and the private sector across the country.
DIKSHA: It was launched on 5th September 2017 by Hon’ble Vice President of India, Shri M. Venkaiah Naidu. The platform aims to enhance teacher training and professional development by accelerating innovative solutions and experiments in education. DIKSHA empowers states and Teacher Education Institutes (TEIs) with the flexibility to customize the platform to meet their specific needs, benefiting teachers, teacher educators, and student teachers across the country.
SWAYAM Plus: SWAYAM Plus, which was officially launched on 27th February 2024 by Shri Dharmendra Pradhan, Hon’ble Minister of Education. The initiative seeks to revolutionize higher education and improve employability by implementing an innovative credit recognition system for industry-relevant courses, emphasizing skill development, employability, and forging stronger industry partnerships.
NISHTHA: The NISHTHA (National Initiative for School Heads’ and Teachers’ Holistic Advancement), launched by the Ministry of Education on 21st August 2019, aims to enhance the professional development of 42 lakh elementary teachers and school heads. In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the program was transitioned to NISHTHA-Online on 6th October 2020, delivered through the DIKSHA platform. Building on this success, in 2021-22, NISHTHA 2.0 was launched for secondary school teachers, while NISHTHA 3.0, focusing on Foundational Literacy and Numeracy, was introduced on 7th September 2021.
NIRF Ranking: The National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF), launched by the Ministry of Education on 29th September 2015, marked a pivotal step toward enhancing the quality and accessibility of higher education in India. NIRF introduced a structured and transparent system for assessing and ranking universities, colleges, and other institutions, fostering healthy competition and encouraging improvements in education and infrastructure.
PM-Vidyalaxmi scheme: The Union Cabinet, led by Hon’ble PM Shri Narendra Modi, has approved the PM-Vidyalaxmi scheme to support meritorious students by providing financial assistance for quality higher education. This scheme offers education loans for students admitted to the top 860 institutions across India, benefiting over 22 lakh students each year. With a budget allocation of Rs. 3,600 crore from 2024-25 to 2030-31, the scheme aims to assist an additional 7 lakh students. Implemented through a fully digital, transparent, and student-centric platform, PM-Vidyalaxmi ensures easy access and smooth interoperability for students nationwide.
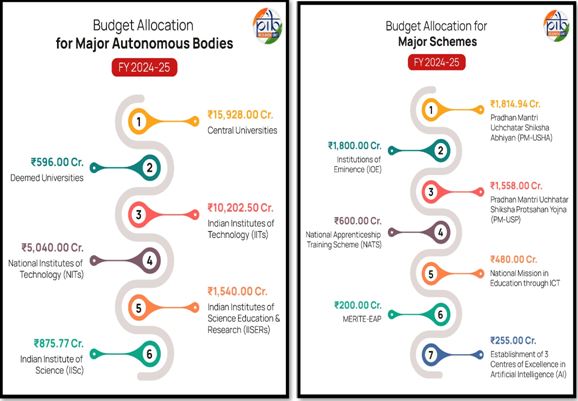
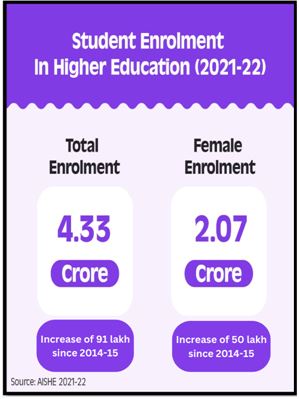
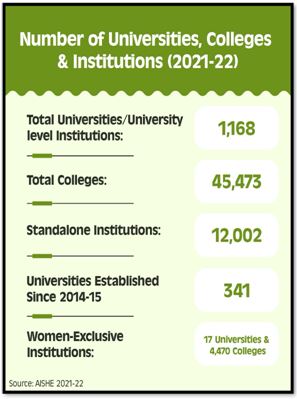
Increase in Enrolment in Higher Education Institutions: AISHE Report 2021-22
Source: PIB
You can find many articles on EDUCATION (part of GS II) in our website. Go through these articles share with your friends and post your views in comment section.
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.Discover more from Simplified UPSC