Daily Insights December 17, 2025
Contents
Daily Insights December 17, 2025
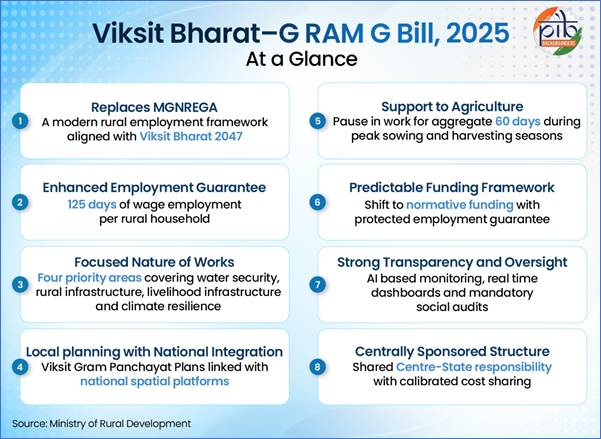
1: VIKSIT BHARAT GUARANTEE FOR ROZGAR AND AJEEVIKA MISSION GRAMIN (GRAMG) BILL 2025
Context
The Union Government has introduced the Viksit Bharat Guarantee For Rozgar and Ajeevika Mission Gramin Bill, 2025 in the Lok Sabha, marking a significant overhaul of rural employment policy. This Bill seeks to replace the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) 2005, which has been India’s flagship rural employment scheme for two decades. The new Bill aligns with the broader vision of Viksit Bharat 2047, aiming to modernize rural employment guarantees while strengthening accountability and linking employment creation with infrastructure and climate resilience goals.
About the Bill
Introduced: December 17, 2025
Replacing: MGNREGA (2005)
Vision: Aligned with Viksit Bharat 2047
Shift in Model: Transforms from demand-driven (MGNREGA) to supply-side driven with fixed allocations
Employment Guarantee: Raises guarantee from current levels to 125 days per annum
Financial Architecture:
Central share: ₹95,692.31 crore (estimated)
State share: 60:40 cost-sharing ratio nationally
Enhanced support: 90:10 for North Eastern and Himalayan states
100% Central funding for Union Territories without legislatures
Total estimated annual requirement: ₹1,51,282 crore
Key Focus Areas: Water-related works, rural infrastructure (roads, connectivity), livelihood infrastructure
Implementation: Clear institutional framework at national, State, district, block, and village levels
Special Features: Digital attendance, wage payments, data-driven planning, enhanced enforcement powers for Centre
Relevance: GS Paper II (Governance & Social Welfare); GS Paper III (Rural Development); Policy formulation and fiscal federalism
Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Rural Development
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressNoteDetails.aspx?id=156553&NoteId=156553&ModuleId=3®=37&lang=1
2: INDIA-JORDAN STRATEGIC PARTNERSHIP AND PM MODI’S BILATERAL VISIT
Context
Prime Minister Narendra Modi completed India’s first full-fledged bilateral visit to Jordan in 37 years, coinciding with the 75th anniversary of India-Jordan diplomatic relations (1950-2025). The visit occurred against the backdrop of instability in West Asia, highlighting Jordan’s role as a moderate stabilizing force in the region. The bilateral engagement demonstrated India’s strategic diversification beyond the Gulf, with a focus on food and fertilizer security, defence cooperation, and people-to-people ties.
About the Visit and Bilateral Relations
Duration: December 15-16, 2025
Significance: First PM bilateral visit in 37 years; 75th anniversary of diplomatic ties
Trade Relations:
Current trade (2023-24): USD 2.875 billion
India’s exports: Cereals, frozen meat, petroleum products, animal fodder
India’s imports: Phosphates, potash (fertilizers)
Proposed target: USD 5 billion in 5 years
Bilateral Agreements: Five MoUs signed:
Renewable energy cooperation
Water resource management
Petra-Ellora heritage twinning
Cultural Exchange Programme (2025-29)
Digital public solutions (population-scale initiatives)
Strategic Cooperation:
Jordan India Fertiliser Company (JIFCO) investment: USD 860 million
Arab Potash Company – IPL MoU: 275,000-325,000 tonnes annually for 5 years
Defence MoU (2018); Naval cooperation; Counter-terrorism collaboration
People-to-People:
ITEC slots: 50 annually
Jordanian graduates from India: 2,500+
Visa on Arrival and e-Visa facilities available
Relevance: GS Paper II (International Relations); West Asia engagement; Middle power diplomacy; South-South cooperation; Bilateral relations
Nodal Ministry: Ministry of External Affairs
Source: https://www.legacyias.com/pib-summaries-17-december-2025/
3: BONDI BEACH SHOOTING – TERRORIST ATTACK WITH INDIAN LINKS
Context
A mass shooting at Bondi Beach in Sydney on December 15, 2025, during a Hanukkah celebration has been formally classified as a terrorist attack motivated by Islamic State ideology. Australian authorities confirmed that the primary perpetrator, a 50-year-old father, was an Indian national from Hyderabad. The attack resulted in 15 deaths and 25 injuries, marking Australia’s deadliest shooting incident in recent years. The investigation has revealed concerning international dimensions, with travel to the Philippines and extremist connections.
About the Incident
Date: December 15, 2025 (Bondi Beach, Sydney)
Death Toll: 15 confirmed deaths (ages ranging from 10 to 87)
Injured: 25 hospitalized (10 in critical condition), including 3 children
Perpetrators Identified:
Father: Sajid Akram, 50 years old (killed at scene)
Son: Naveed Akram, 24 years old (hospitalized; charged with 59 offences including 15 counts of murder and terrorist act)
Attacker’s Background:
Father’s nationality: Indian (from Hyderabad)
Indian passport holder
Moved to Australia in 1998
Legally possessed 6 firearms
Travel to Philippines: November 1-28, 2025 (with son)
Evidence of Radicalization:
ISIS flags recovered from vehicle
Homemade explosive devices found
Planned targeting of Jewish community
Islamic State ideology motivation
Heroes: Ahmed al-Ahmed (bystander, Syrian) disarmed one attacker; Bondi lifeguards assisted rescue operations
Investigation Status: Inter-agency coordination between Australian and Indian law enforcement; Philippine authorities involved in probe of suspects’ travel
Relevance: GS Paper II (International Relations; Diaspora security); GS Paper III (Internal Security; Counter-terrorism); International crime and cooperation
Related Agencies: Australian Federal Police; INTERPOL; External Affairs Ministry
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/Press
4: INDIAN RUPEE HITS RECORD LOW OF 91 AGAINST US DOLLAR
Context
The Indian rupee breached the critical 91-per-US dollar mark for the first time in history, marking a significant depreciation milestone. The rupee fell from 90 to 91 in just 10 trading sessions, losing over 1% in a span of five days. This represents a year-to-date depreciation of 6.2%, making it one of Asia’s worst-performing currencies in 2025. The weakness is driven by sustained foreign portfolio investor outflows, global macro uncertainties, and delays in US-India trade deal finalization.
About the Currency Crisis
Date: December 16-17, 2025
New Record Low: 91.14 (intra-day low); 91.075 (closing)
Previous Low: 90.78 (December 2025)
Year-to-Date Performance:
Depreciation: 6.2% (worst among regional peers)
Indonesian rupiah: -3.53%
Philippine peso: -1.54%
Key Causes:
Foreign Portfolio Investor (FPI) outflows: ₹4,335 Cr (first 2 days of Dec); ₹19 billion year-to-date; ₹2.7 billion (first 2 weeks of Dec)
Uncertainty over US-India trade deal
Persistent dollar demand for NDF maturities
US tariff tensions (50% tariffs on Indian imports announced)
Lack of clarity on trade negotiations
Implications:
Increased import costs: Fuel, electronics, essentials becoming expensive
Benefits for exporters and NRIs (higher remittances)
Macroeconomic concerns amid external vulnerabilities
RBI’s measured approach: Allowing gradual depreciation rather than aggressive intervention
Relevance: GS Paper III (Indian Economy – External Sector); Forex management; Capital flows; Trade dynamics
Nodal Agency: Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
5: NATIONAL PROJECT FOR DISASTER RISK REDUCTION AT PANCHAYAT LEVEL
Context
The Union Government has approved a major initiative to strengthen community-based disaster risk reduction at the grassroots level. A High-Level Committee, chaired by Union Home Minister and Minister of Cooperation Amit Shah, has approved ₹507.37 crore for implementing the National Project for Strengthening Community Based Disaster Risk Reduction Initiatives in Panchayati Raj Institutions across 20 states. This represents an extension of the National Disaster Mitigation Fund (NDMF) to the panchayat level, enhancing India’s disaster preparedness infrastructure.
About the Scheme
Approved Date: December 16, 2025
Chairperson: Amit Shah (Union Home Minister & Minister of Cooperation)
Coverage: 20 States across India
Financial Outlay:
Total Project Cost: ₹507.37 crore
Central Share (NDMF): ₹273.38 crore
State Share: ₹30.37 crore
Ministry of Panchayati Raj Contribution: ₹151.47 crore
State Share (MoPR): ₹52.15 crore
Implementation:
Nodal Agency: National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
Collaborative Effort: Ministry of Panchayati Raj + NDMA
Framework: Community-based approach at village level
Institutional Structure: Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs)
Broader Context:
Extension of NDMF (launched 2021) to local governance level
Comprehensive disaster financing system already in place:
State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF) FY 2025-26: ₹16,118 crore released to 28 States
National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF) FY 2025-26: ₹2,854.18 crore to 18 States
State Disaster Mitigation Fund (SDMF): ₹5,273.60 crore to 21 States
National Disaster Mitigation Fund: ₹1,423.06 crore to 14 States
Relevance: GS Paper II (Disaster Management & Governance); GS Paper III (Internal Security & Resilience); Federalism and local governance
Nodal Ministries: Ministry of Home Affairs; Ministry of Panchayati Raj; NDMA
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2204819®=6&lang=1
6: STRATEGIC NUCLEAR POWER BILL 2025 (SHANTI BILL)
Context
The Union Government has introduced the Strategic Nuclear Power Infrastructure (SHANTI) Bill in Parliament, proposing a historic shift in India’s nuclear energy policy by enabling private sector participation in nuclear power generation. The move aims to accelerate India’s journey toward 100 GW of nuclear capacity by 2047, while maintaining national security safeguards and public interest protection. The Bill represents a pragmatic approach to bridging resource constraints and shortening project gestation periods.
About the Bill
Introduced: December 17, 2025 (Lok Sabha)
Full Name: Strategic Nuclear Power Infrastructure (SHANTI) Bill, 2025
Purpose: Private and joint venture participation in nuclear energy generation
Key Objectives:
Scale up nuclear energy generation to meet rising demand
Bridge resource constraints in public sector
Shorten project gestation periods
Support national target: 100 GW nuclear capacity by 2047
Ensure responsible private participation without compromising security
Critical Features:
Supplier liability limitations (as per international norms)
National security safeguards maintained
Public interest protection provisions
Departmental Oversight:
Presented by: Dr. Jitendra Singh (Minister, Department of Atomic Energy)
Department of Atomic Energy budgetary increase: 170% increase over past decade
Installed nuclear capacity: Doubled since 2014
Strategic Rationale:
Current nuclear contribution to energy mix remains modest compared to global peers
Rising demand from sectors: Data processing, healthcare, industry, alongside renewables
Data centers particularly energy-intensive
Relevance: GS Paper III (Energy Security; Nuclear Power; Infrastructure); GS Paper II (Governance & Policy); Strategic infrastructure development
Nodal Ministry: Department of Atomic Energy (DAE)
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2205519®=6&lang=1
7: DEADLY CYCLONES AND FLOODS ACROSS SOUTH AND SOUTHEAST ASIA
Context
South and Southeast Asia experienced catastrophic flooding and landslides triggered by severe cyclones and monsoon rains in December 2025, particularly affecting Sri Lanka, Malaysia, Thailand, and Indonesia. The natural disasters killed over 1,600 people across multiple countries, displaced thousands, and caused unprecedented environmental damage. Scientific analysis confirms that climate change intensified the rainfall patterns and flooding severity, while deforestation and rapid urbanization exacerbated the disasters’ impact on communities and biodiversity-rich ecosystems.
About the Disasters
Timeline: Early-to-mid December 2025
Primary Cyclones: Senyar (Sumatra, Indonesia); Ditwah (Sri Lanka)
Death Toll: Over 1,600 confirmed deaths across affected countries
Affected Regions:
Sri Lanka (central highlands)
Malaysia
Thailand
Indonesia (Sumatra region)
Climate Attribution:
World Weather Attribution study finding: Climate change made rainfall more likely and intense
Deforestation and rapid urbanization compounded impacts
Monsoon rains intensified beyond “normal” levels
Environmental Consequences:
Cyclone Senyar (Sumatra): Deforestation + mining + plantations + peat drainage left watersheds unable to absorb intense rainfall
Cyclone Ditwah (Sri Lanka):
Extensive damage to biodiversity-rich central highlands
Knuckles mountain range (UNESCO biodiversity hotspot) severely impacted
Flooding and landslides in sensitive ecosystems
Indonesia: Extinction-level disturbance for Tapanuli orangutan (world’s rarest great ape)
Key Vulnerability Factors:
Decades of deforestation reducing watershed absorption capacity
Mining activities degrading landscape
Peat drainage eliminating natural water storage
Rapid urbanization without proper drainage infrastructure
Climate change intensifying precipitation patterns
Relevance: GS Paper III (Climate Change & Environmental Disasters); GS Paper I (Geomorphology & Natural Disasters); Biodiversity conservation
Reporting Agencies: World Weather Attribution; UN agencies; Environmental monitoring networks
8: EDITORIAL ANALYSIS – INDIA AND THE US: 2005 VERSUS 2025
Context
The Hindu paper’s editorial offers a comparative analysis of India-US strategic relations across two pivotal moments: 2005 (characterized by American confidence and strategic generosity toward India’s rise) and 2025 (marked by American retrenchment and focus on burden-minimization). This editorial reflects a significant strategic shift, examining how the broader transformation in American foreign policy impacts India’s strategic autonomy and global positioning within the evolving international order.
About the Editorial Analysis
Publication: The Hindu Editorial, December 17, 2025
Comparative Framework:
2005 Doctrine: US viewed India’s rise as a strategic objective; Generosity and partnership ethos
2025 Reality: US focused on minimizing burdens; Retrenchment from internationalism
Key 2005 Characteristics:
American self-assurance and strategic generosity
Washington sought to help India become a major world power
Rise of India viewed as stabilizing global force
Mutual confidence embedded in partnership
Civil nuclear agreement exemplified expansive vision
Strategic autonomy accommodated within shared optimism
Global leadership viewed as responsibility, not liability
2025 Strategic Shift:
US National Security Strategy (NSS) more inward-looking
American focus shifted to reassuring itself of relevance
Minimization of international commitments
Burden-shifting (rather than burden-sharing) approach
India reframed: From strategic end to tactical means
India used as component in China-balancing strategy (Quad framework)
Implications for India:
India no longer recipient of strategic sponsorship for its rise
External sponsorship cannot be assumed
Must rely on own strategic confidence and material capacity
Broader strategic space created by contracting American ambitions
Need for recalibration of India’s strategic outlook
Historical Lesson:
Assumptions of 2005 may not return
India’s challenge: Craft role aligned with its scale, interests, and civilisational temperament
Paradox: American retrenchment creates greater autonomy for India
Relevance: GS Paper II (International Relations); US foreign policy; Strategic autonomy; India’s global positioning
Source: The Hindu Editorial, December 17, 2025
Source: https://vajiramandravi.com/current-affairs/daily-editorial-analysis-17-december-2025/
9: VIKSIT BHARAT SHIKSHA ADHISHTHAN (VBSA) BILL – HIGHER EDUCATION REFORMS
Context
The Union Government has proposed the Viksit Bharat Shiksha Adhishthan (VBSA) Bill, 2025, seeking to replace the University Grants Commission (UGC) and fundamentally reform India’s higher education regulatory framework. The Bill has been proposed for examination by a Joint Parliamentary Committee (JPC) following significant opposition from Parliament members and civil society, who raised concerns about excessive government control, reduced institutional autonomy, and punitive compliance mechanisms.
About the Bill
Introduced: December 2025 (Lok Sabha)
Proposing Body: Union Ministry of Education
Education Minister: Dharmendra Pradhan
Target: Replace University Grants Commission (UGC)
Referred To: Joint Parliamentary Committee (JPC) for scrutiny
Scope of Change:
Complete overhaul of higher education regulation in India
New institutional framework replacing 70+ year old UGC structure
Opposition Concerns:
Excessive government control over institutions
Reduction in institutional autonomy
Strict compliance regime with harsh penalties
Centre empowered to close non-compliant institutions
Centralization of decision-making authority
Concerns over academic freedom
Proponents’ Arguments:
Aligns with Viksit Bharat 2047 vision
Modernizes outdated UGC framework
Improves regulatory efficiency
Strengthens accountability mechanisms
Relevance: GS Paper II (Education Policy & Governance); GS Paper III (Higher Education Regulation); Constitutional provisions on education
Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Education (Department of Higher Education)
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/; https://ambitiousbaba.com/the-hindu-editorial-analysis-17th-december-2025/
10: INDIA-MALDIVES JOINT MILITARY EXERCISE EKUVERIN CONCLUDES
Context
India-Maldives bilateral military exercise EKUVERIN (meaning “friendship” in Malayalam) has concluded, reaffirming the strategic defence partnership between the two nations. The exercise underscores India’s commitment to regional maritime security, neighbourhood policy priorities, and capacity building in the Indian Ocean region. This military cooperation is particularly significant given evolving geopolitical dynamics in South Asia and the Indian Ocean.
About the Exercise
Exercise Name: EKUVERIN (meaning “friendship” in Malayalam)
Completion Date: December 17, 2025 (concluded during this period)
Bilateral Participants: India and Maldives
Scope: Joint military exercise with inter-services coordination
Significance:
Reaffirms defence partnership
Demonstrates shared commitment to maritime security
Aligns with India’s Neighbourhood First policy
Part of broader Indian Ocean security framework
Capacity building and interoperability enhancement
Strategic Context:
Bilateral military relations strengthened
Response to regional security dynamics
Focus on maritime domain awareness
Mutual security interests in Indian Ocean
Previous Cooperation: Continuation of regular military exercises
Relevance: GS Paper II (International Relations; Bilateral Relations); GS Paper III (Defence & Internal Security; Maritime Security); Neighbourhood policy
Nodal Agencies: Ministry of Defence; Indian Navy; Maldivian armed forces
Source: https://www.thecoreias.com/17-december-2025-what-to-read-in-the-hindu/
11: EGYPT-ISRAEL NATURAL GAS EXPORT DEAL – USD 35 BILLION AGREEMENT
Context
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu has approved a historic long-term natural gas export deal with Egypt, marking a significant strategic and economic development in Middle East energy politics. The agreement involves exporting USD 35 billion worth of natural gas from Israel’s Leviathan gas field to Egypt over 15 years, representing one of the region’s largest energy cooperation agreements and carrying implications for regional stability and international energy markets.
About the Deal
Announcement Date: December 17, 2025
Approval Authority: Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu
Duration: 15-year contract
Value: USD 35 billion
Energy Source: Leviathan Gas Field (Israeli offshore territory)
Exporting Country: Israel
Importing Country: Egypt
Strategic Significance:
Largest energy deal between Israel and Egypt in recent years
Egypt benefits from energy security and export revenue potential
Israel secures long-term energy markets and revenue
Regional cooperation in energy sector despite political tensions
Demonstrates economic pragmatism amid geopolitical challenges
Broader Context:
Mediterranean energy politics
Regional supply chain security
Long-term energy contracts amidst regional volatility
International energy cooperation frameworks
Relevance: GS Paper II (International Relations; West Asia); GS Paper III (Energy Security; Natural Resources); Strategic partnerships
Key Players: Israel, Egypt, Energy markets
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Current_events/2025_December_17
12: TRUMP ADMINISTRATION EXPANDS TRAVEL BAN TO 20 ADDITIONAL COUNTRIES
Context
US President Donald Trump has announced a significant expansion of the country’s travel restrictions by implementing additional travel bans affecting at least 20 more countries. The expanded ban includes complete restrictions on citizens from Burkina Faso, Mali, South Sudan, and Syria, as well as those holding passports issued by the Palestinian Authority, while partial restrictions have been imposed on citizens from 15 other countries. This represents a major shift in US immigration and security policy with far-reaching international implications.
About the Travel Ban
Announcement Date: December 17, 2025
Ordering Authority: President Donald Trump
Scope of Expansion: 20 additional countries (beyond existing ban list)
Complete Bans Imposed On:
Burkina Faso
Mali
South Sudan
Syria
Palestinian Authority (passport holders)
Partial Restrictions On: 15 other nations (criteria-based restrictions)
Geographic Impact:
Africa hardest hit (Burkina Faso, Mali, South Sudan)
Middle East impacted (Syria)
Palestinian territories directly affected
Global reach across multiple regions
Implementation Framework:
Travel restrictions based on security assessments
Criteria-based determination for partial restrictions
National security justification provided
International Reactions:
African countries express muted reactions despite significant impact
Diplomatic tensions with affected nations
Concerns over refugee and asylum processes
Policy Shift Rationale:
Border security
Terrorism prevention
Immigration enforcement
Relevance: GS Paper II (International Relations; Bilateral Relations); Immigration and asylum issues; Human rights concerns
Implementing Authority: US Department of State; Department of Homeland Security
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Current_events/2025_December_17
Discover more from Simplified UPSC
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.