PREHISTORIC INDIA
PREHISTORIC INDIA refers to the history of human settlements in India during the prehistoric time (Before BCE 3000) when there was no writing and development. It consists of five major phases
- Paleolithic,
- Mesolithic,
- Neolithic,
- Chalcolithic &
- Iron Age.
Human travel
25,00,000 BC in Africa
500,000 BC in India
300,000 BC discovery of Fire
| History divided into | |
| 1. Pre-history | Before invention of writing Before Harappan and vedic culture |
| 2. Proto-History | Invention of connotations and letters Harappan and vedic culture |
| 3. History | The study of the past after the invention of writing and the study of literate societies based on the written and archaeological sources constitutes history. |
Robert Bruce Foote
The father of Indian prehistory
Foote joined the Geological Survey of India (GSI) on 29 December 1858 was posted in the Madras Presidency, Hyderabad region and Bombay. In 1887 he became a Director of the GSI and on retiring in 1891, he joined the state of Baroda.
Discovered what was probably the first palaeolithic tool discovered in India — the Pallavaram handaxe

Contents
Stone Age divided into three period:
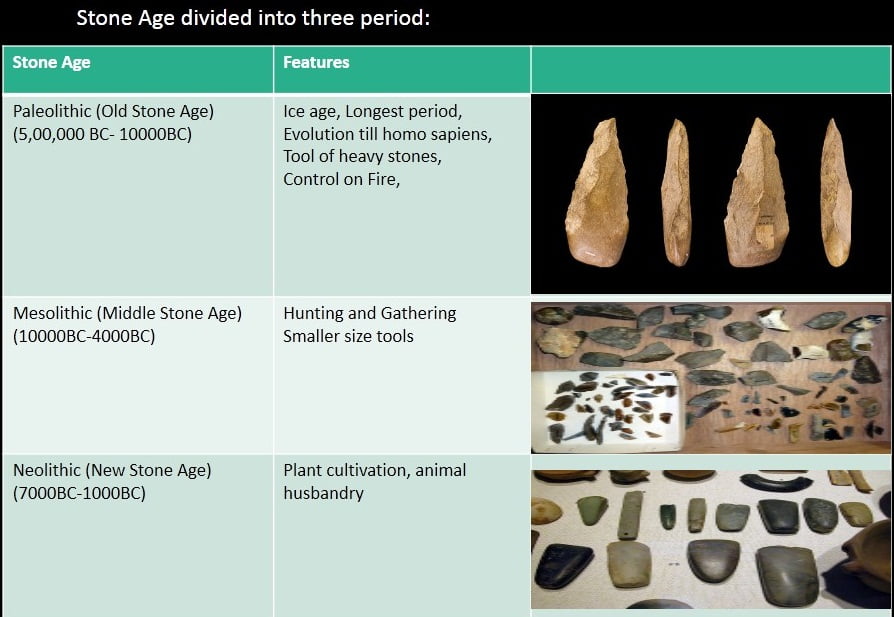
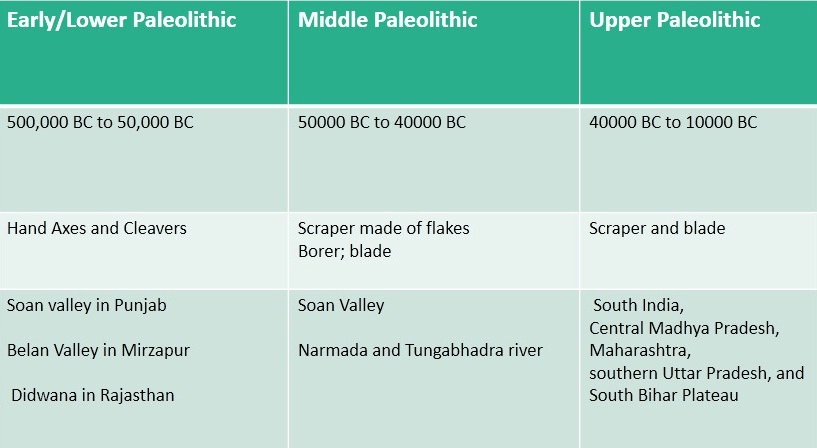
I. Paleolithic (Old Stone Age)
- The term Plaeolithic was coined by Archaeologist John Lubbock in 1865.
- Period 500000-10000 BC
- Hunters and Food Gatherers
- used unpolished, undressed rough stones
- Lingsugur in Raichur district, Karnataka was the first site to be discovered from India.’
- Except plains of Indus, Ganga and Brahmaputra
- Material used for making tools was mainly quartzite and chert but quartz and basalt also used
- The ostrich egg shells at over 40 sites
- Paleolithic sites in India
- Lidder river Pahalgam , Kashmir
- Soan valley Punjab,
- Banks of River Beas, Banganga, Sirsa Haryana,
- Chittorgarh and Kota, Rajasthan,
- River Wagoon, Kadamali basins; Sinsgi Talav, Didwana , Nagaur Rajasthan
- River Sabaramati and Mahi basins (Rajasthan & Gujarat),
- Basins of river tapti, Godavari, Bhima and Krishna; Koregaon, Chandoli and shikarpur (Maharashtra),
- River Raro (Jharkhand),
- River Suvarnrekha (Orissa),
- Ghatprabha River Basin (Karnataka).
- Belan Valley, Allahabad
- Hunsgi, Gulbarga in Karnataka.
- Attirampakkam in Tamilnadu
Belan Valley: All three phases of Paleolithic period followed by Mesolithic and then by Neolithic have been found in sequence.

Climatic conditions during Paleolithic Period:
- There was extremely cold and arid climate in the high altitude and northern latitudes.
- There was extensive formation of deserts in North west India
- The drainage pattern of western India became almost defunct and river courses shifted “westwards”.
- Vegetation cover over most of the country thinned out during this period.
- Coastal areas of south-eastern Tamil Nadu, Saurashtra and Kutch developed quartz and carbonate dunes as a result of the lowering of the sea level.
- During terminal Pleistocene south-westerly monsoons became weak and the sea level decreased by scores of metres.
II. Mesolithic Age
• 10000BC-4000BC
• End of Ice Age ; Warm and Humid climate
•Increased rainfall
•Expansion of Flora and Fauna
•Availability of new resources to humans (increased in population)
•First human colonization on the Ganga plains took place during this period
•Transitional phase between Paleolithic Age and Neolithic Age
•The Mesolithic tools smaller in size and better in finishing (more geometric)
•Microliths ; not more than five centimeter (spearheads, arrowheads, knives; bow and arrows paintings)
•shallow querns and grinding stones

Disposal of dead and making of Graves
• The first evidence of intentional disposal of the dead
• Mesolithic human burials
• Bagor in Rajasthan, Langhnaj in Gujarat, Bhimbetka in Madhya Pradesh etc
• Buried in graves both in extended and crouched position
{in crouched position knees are bent and the upper body is brought forward and down}
• In some cases two individuals were buried in a single grave
• Grave offerings: chunks of meat, grinding stones, stone, bone and antler ornaments
Mesolithic Art
•Several thousand rock shelters in the vindhyan sandstone hills
•Bhimbetka and jogimara caves
•Mostly in red and white pigments
•Mostly wild animals and hunting scenes,
•Human social and religious life such as sex and child birth
Important Mesolithic Sites
| State/Part | Sites |
| Rajasthan | Bagor (Largest); Tilwara, Pachpadra basin and Sojat Area |
| Gujarat | Banks of river Sabarmati such as Akhaj, Valsana, Hirpur, Langhanj etc |
| Uttar Pradesh | Belan Valley, Sarai Nahar Rai, Morhana Pahar and Lekkahia |
| Madhya Pradesh | Bhimbetka along with Adamgarh, Chaturbhujnath Nala |
| Jharkhand | Chhota nagpur plateau |
| Odisha | Mayurbhanj, Keonjhar, Sundergarh |
| South India | Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh |
Neolithic Age in India
Chalcolithic age
Discover more from Simplified UPSC
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.