Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO)
Context:
National Security Advisor Ajit Doval has proposed an action plan against Pakistan-based terror groups Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT) and Jaish-e-Mohammad (JeM) as part of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO)-NSAs meet.
Contents
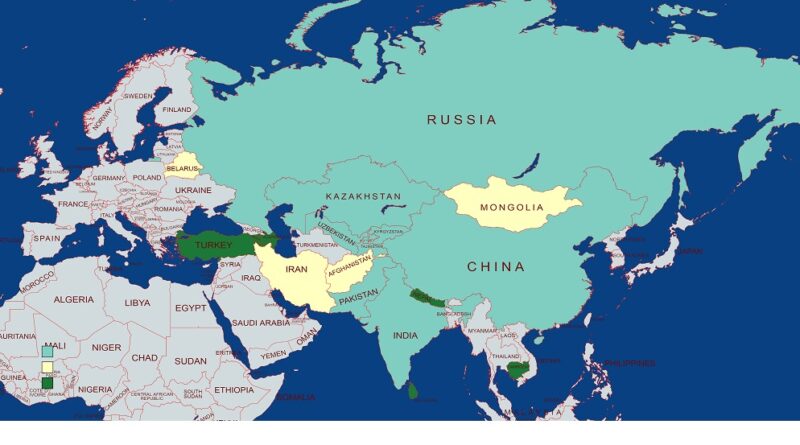
About Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) :
- The Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), or Shanghai Pact, is a political, economic, and security alliance.
- The creation of which was announced on 15 June 2001 in Shanghai,
- Founding members China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan.
- The Shanghai Cooperation Organization Charter, formally establishing the organization, was signed in June 2002 and entered into force on 19 September 2003.
- The original five members, with the exclusion of Uzbekistan, were previously members of the Shanghai Five group, founded on 26 April 1996. Since then, the organization has expanded its membership to eight states when India and Pakistan joined SCO as full members on 9 June 2017 at a summit in Astana, Kazakhstan.
- the SCO comprises eight member states, namely the Republic of India, the Republic of Kazakhstan, the People’s Republic of China, the Kyrgyz Republic, the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, the Russian Federation, the Republic of Tajikistan, and the Republic of Uzbekistan;
- 4 Observer States interested in acceding to full membership: Afghanistan, Belarusm, Iran, Mongolia
- 6 Dialogue Partners: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Cambodia, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Turkey
- The Heads of State Council (HSC) is the supreme decision-making body in the SCO.
- It meets once a year and adopts decisions and guidelines on all important matters of the organization.
- Military exercises are also regularly conducted among members to promote cooperation and coordination against terrorism and other external threats, and to maintain regional peace and stability.
- The SCO is the largest regional organization in the world in terms of geographical coverage and population, covering three-fifths of the Eurasian continent and nearly half of the human population.
- Criticisms of the SCO include that it is used by member states to shield each other from international criticism regarding human rights violations.
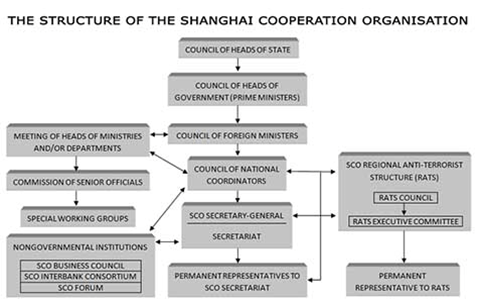
Structure of the SCO
Objectives of the SCO
- Strengthening mutual trust and neighborliness among the member states.
- Promoting effective cooperation in -politics, trade & economy, research & technology and culture.
- Enhancing ties in education, energy, transport, tourism, environmental protection, etc.
- Maintain and ensure peace, security and stability in the region.
- Establishment of a democratic, fair and rational new international political & economic order.
Guiding Principle – Based on Shanghai Spirit
- Internal policy based on the principles of mutual trust, mutual benefit, equality, mutual consultations, respect for cultural diversity, and a desire for common development.
- External policy in accordance with the principles of non-alignment, non-targeting any third country, and openness.
Strengths of Shanghai Corporation Organization
- The SCO covers 40%of the global population, nearly 20% of the global GDP and 22% of the world’s land mass.
- The SCO has a strategically important role in Asia due to its geographical significance – this enables it to control the Central Asia and limit the American influence in region.
- SCO is seen as counterweight to the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation.
Discover more from Simplified UPSC
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.